Exercise Science Major: Complete Guide to Difficulty, Requirements, and Career Prospects

Understand exercise science as an academic field
Exercise science represent an interdisciplinary field that combine biology, chemistry, physics, and psychology to study human movement and physical activity. Students pursue this major dive abstruse into how the body respond to exercise, the mechanisms behind physical performance, and the role of activity in health promotion and disease prevention.
The curriculum typically encompasses anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, exercise psychology, nutrition, and research methods. Universities structure these programs to prepare graduates for careers in fitness, rehabilitation, sports performance, and health promotion sectors.
Academic rigor and course difficulty
Exercise science programs demand strong foundational knowledge in multiple scientific disciplines. Students must master complex concepts in human anatomy and physiology, understand intricate body systems and their interactions during physical activity.
Core science requirements
Most programs require extensive coursework in biology, chemistry, and physics. Students typically complete general biology, anatomy and physiology sequences, general chemistry, and physics courses. These prerequisites establish the scientific foundation necessary for advanced exercise science concepts.
Mathematics requirements oftentimes include statistics and sometimes calculus, depend on the institution. Research methodology courses teach students to design studies, analyze data, and interpret scientific literature critically.
Specialized exercise science courses
Advanced coursework cover exercise physiology, biomechanics, motor learning, and exercise psychology. These classes integrate basic science knowledge with practical applications in human movement and performance.
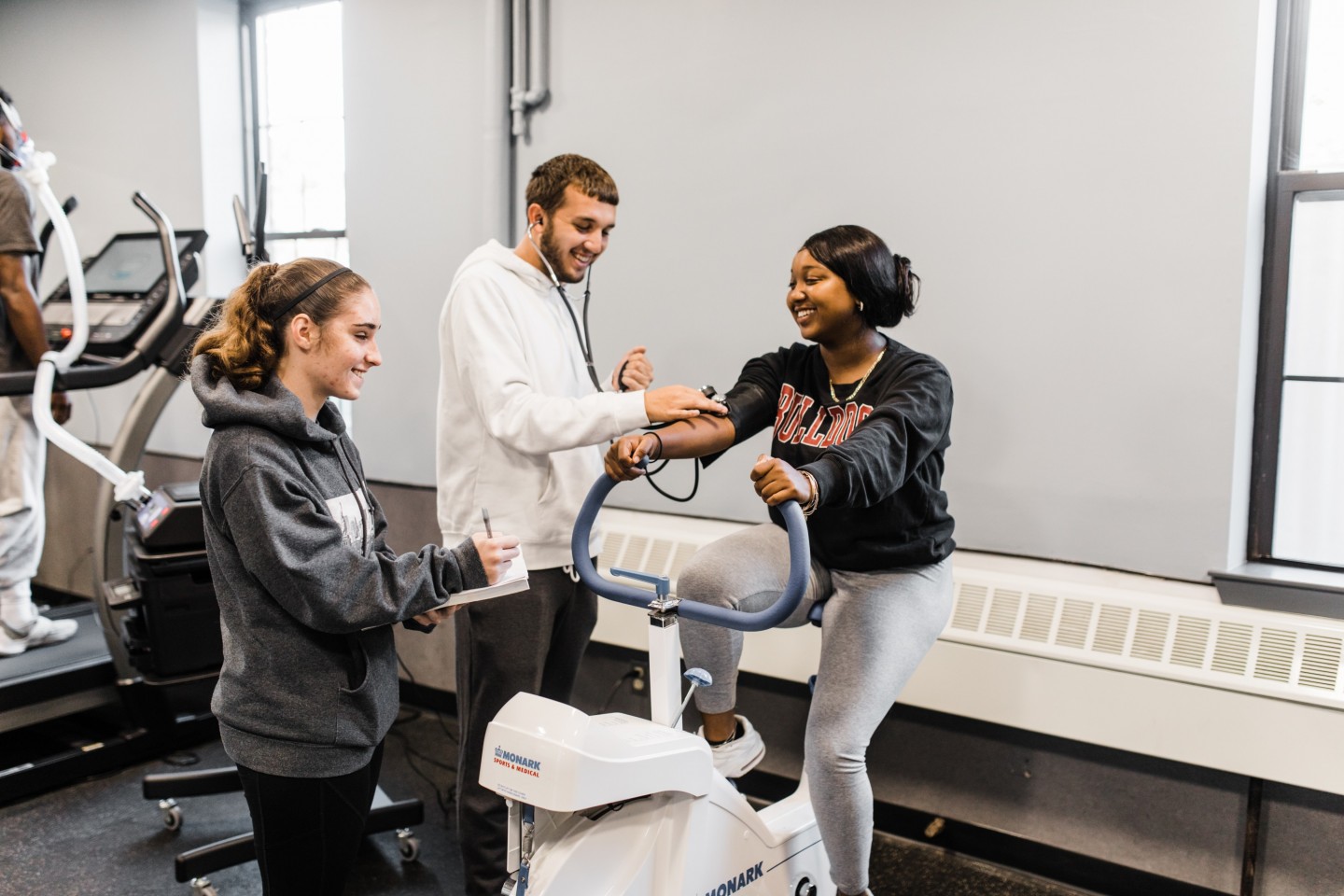
Laboratory components accompany most courses, require hands-on experience with equipment like metabolic carts, force plates, electromyography systems, and body composition analyzers. Students learn to conduct fitness assessments, design exercise programs, and interpret physiological data.
Comparison to other health relate majors
Exercise science difficulty levels vary compare to other health and science majors. The program typically requires less intensive chemistry and mathematics thanpre-medicall tracks but more rigorous science coursework than general health studies programs.
Compare to nursing programs, exercise science may have fewer clinical hours but require deeper understanding of exercise physiology and biomechanics. Kinesiology programs oftentimes overlap importantly with exercise science, though some institutions differentiate between the two fields.
Skills and aptitudes for success
Students who excel in exercise science programs typically possess strong analytical thinking skills and genuine interest in human biology and movement. Effective communication abilities prove essential, as graduates frequently work forthwith with clients, patients, or athletes.
Essential academic skills
Success require solid foundation in scientific reasoning and problem-solving. Students must synthesize information from multiple disciplines and apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations.
Laboratory skill development include equipment operation, data collection, and analysis. Many programs emphasize hands on learn through internships, practicums, or undergraduate research opportunities.
Personal characteristics
Successful students frequently demonstrate passion for fitness, health promotion, or athletic performance. Attention to detail prove crucial when conduct assessments or design exercise interventions.
Interpersonal skills matter importantly, as many career paths involve work with diverse populations in various settings. Cultural competency and empathy enhance effectiveness in client interactions.
Time management and study strategies
Exercise science programs require substantial time commitment for both classroom learning and laboratory work. Students must balance theoretical coursework with practical skill development and frequently complete internship requirements.
Effective study strategies include form study groups for complex physiology concepts, utilize laboratory time expeditiously, and seek faculty mentorship for research opportunities. Many students benefit from create visual aids for anatomical structures and physiological processes.

Source: ohiohipoint.com
Career preparation and professional development
The major prepare students for diverse career paths in fitness, healthcare, research, and education. Graduates oft pursue certifications from organizations like the American college of sports medicine, national strength and conditioning association, or American council on exercise.
Graduate school preparation
Many students use exercise science as preparation for advanced degrees in physical therapy, occupational therapy, medicine, or specialized graduate programs in exercise physiology or biomechanics.
Research experience through undergraduate programs enhance graduate school applications. Students should seek opportunities to present at conferences or contribute to faculty research projects.
Direct entry career paths
Bachelor’s degree holders can pursue careers as fitness trainers, exercise physiologists, wellness coordinators, or strength and conditioning specialists. Some positions require additional certifications or specialized training.
Corporate wellness, cardiac rehabilitation, and sports performance represent grow employment sectors for exercise science graduates.
Financial considerations and return on investment
Exercise science programs typically cost similar amounts to other bachelor’s degree programs at the same institutions. Students should consider potential earning trajectories when evaluate program investment.
Entry level positions may offer modest starting salaries, but advancement opportunities and specialization can importantly increase earn potential. Geographic location and employment sector greatly influence compensation levels.
Technology integration and modern developments
Contemporary exercise science programs progressively incorporate technology training, include wearable devices, mobile applications, and sophisticated laboratory equipment. Students learn to utilize heart rate monitors, accelerometers, and software for movement analysis.

Source: salisbury.edu
Virtual reality and artificial intelligence applications in exercise and rehabilitation represent emerge areas require technological literacy alongside traditional exercise science knowledge.
Internship and practical experience requirements
Most programs mandate internship experiences in relevant professional settings. Students might complete rotations in fitness centers, rehabilitation clinics, sports teams, or research laboratories.
These experiences provide network opportunities, practical skill application, and career exploration. Strong performance during internships oftentimes lead to employment offers or valuable professional references.
Professional networking and organizations
Student involvement in professional organizations like the American college of sports medicine provide access to conferences, continue education, and network opportunities. Many universities have student chapters that facilitate professional development.
Build relationships with faculty, practice professionals, and fellow students create valuable networks for career advancement and collaborative opportunities.
Specialization options within the field
Exercise science students can focus on specific populations or applications, such as pediatric exercise, geriatric fitness, clinical exercise physiology, or sports performance. Specialization oftentimes occur through elective coursework, internship selection, or undergraduate research focus.
Some programs offer concentrations in areas like pre physical therapy, fitness management, or exercise psychology, allow students to tailor their education toward specific career goals.
Make the decision: is exercise science right for you?
Prospective students should frankly assess their interest in scientific coursework, comfort with laboratory settings, and career aspirations. Shadowing professionals, volunteer in relevant settings, or take introductory courses can provide valuable insights.
Consider whether you prefer direct client interaction, research activities, or administrative roles within the health and fitness industry. Exercise science offer flexibility for various career directions while require solid scientific foundation.
The field continue to evolve with advance technology, grow health consciousness, and expand understanding of exercise’s role in disease prevention and treatment. Students enter exercise science programs position themselves within a dynamic, grow profession that straight impact public health and individuwell-beinging.